5G NR 测试——准备好迎接 5G 挑战了吗?
5G NR 部署正在快速展开,挖掘出新的使用场景和各种应用领域,为新设备和基础设施制造了大量机遇
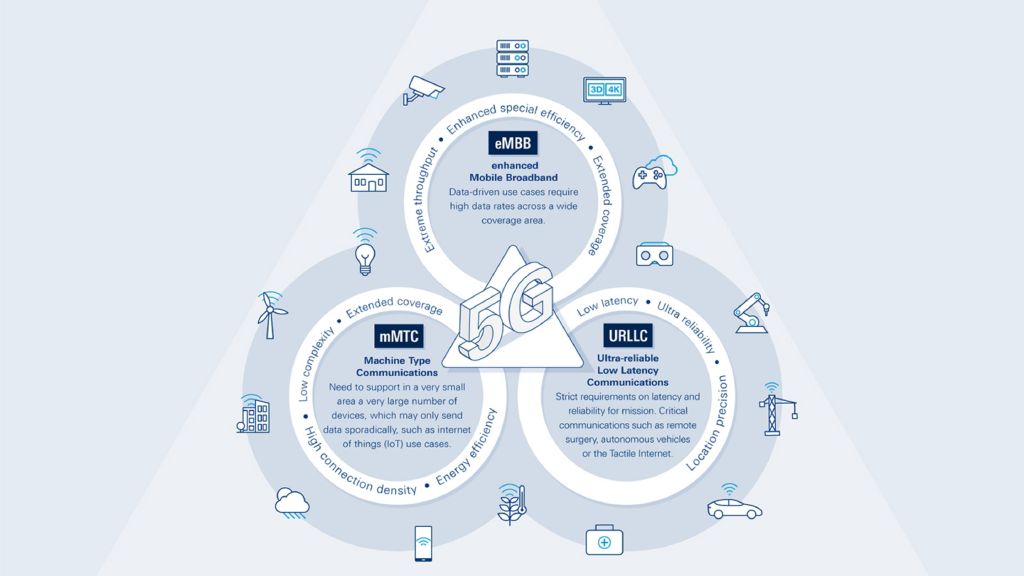
5G 颠覆了通信方式。5G 推动向以用户和应用为中心的技术框架的转变,旨在增强系统效率、实现优越的灵活性,并支持三种重要用例:
- 增强型移动宽带 (eMBB) 满足不断增长的对更快、更大容量的数据访问的需求,让连接无处不在。
- 大规模物联网 (mMTC) 重点关注为海量设备之间的通信提供支持,这些设备通常是物联网 (IoT) 传感器,它们会传输少量数据,不需要实时通信。
- 超可靠低延迟通信 (URLLC) 支持数据交换以提供可靠、重要的通信服务,例如工业物联网、汽车安全和健康监测,需要保证低延迟和出色的网络恢复能力。